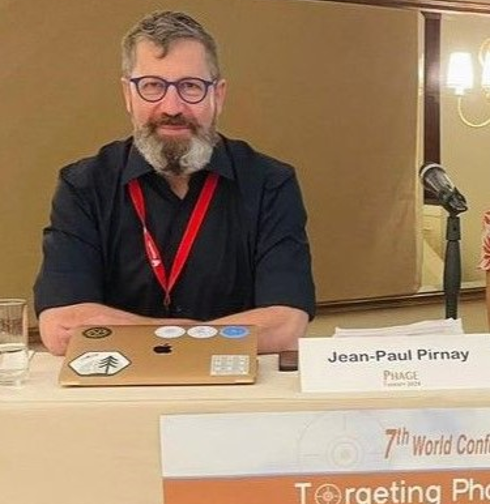
The Targeting Phage Therapy 2024 Best Scientific Contribution award was discerned to:
Jean-Paul Pirnay, Queen Astrid Military Hospital, Belgium
Dr. Pirnay, an active scientific board member, concluded the conference and presented an insightful presentation titled “Magistral Phage Preparations – Is This the Model for Everyone?”
In his presentation, Dr. Pirnay explored:
🔹 Phage therapy as a tool against antimicrobial resistance
🔹 Challenges with industrially manufactured phage products
🔹 Belgium’s national framework for personalized phage products
🔹 Potential for other countries to adopt similar frameworks
Dr. Pirnay’s extensive expertise in phage therapy and antimicrobial resistance continues to drive innovations in personalized phage treatments. His significant contributions to the field and the conference have been invaluable.
Congratulations to Dr. Pirnay on his well-deserved award and for advancing the field of personalized phage therapy.
You can learn about Dr. Pirnay’s insightful research to benefit from his experience in the Targeting Phage Therapy 2024 Replay and Abstracts Book.
Targeting Phage Therapy 2024 Congress
7th World Conference
June 20-21, 2024 – Malta