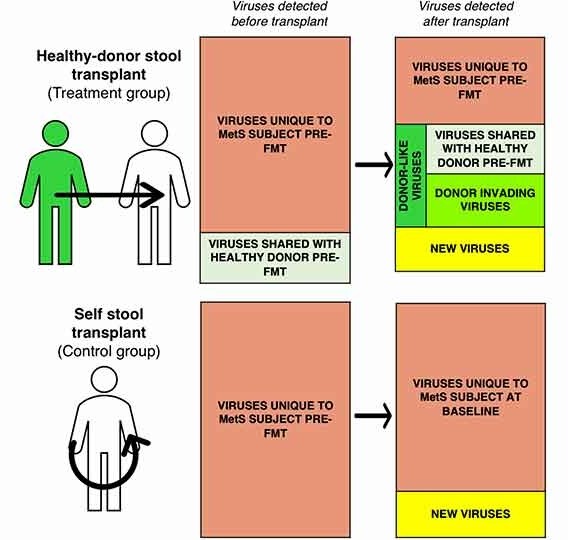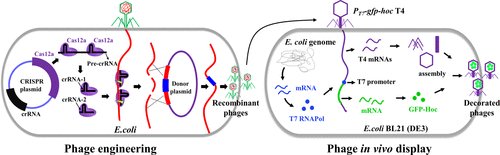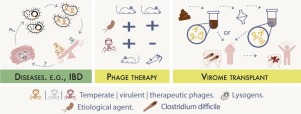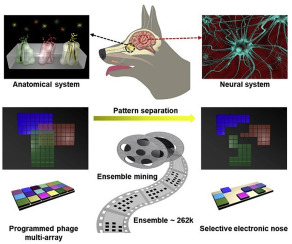
Bacteriophage Cocktails in the Post-COVID Rehabilitation
Increasing evidence suggests that gut dysbiosis is associated with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection and may persist long after disease resolution. The excessive use of antimicrobials in patients with COVID-19 can lead to additional destruction of the microbiota, as well as to the growth and spread of antimicrobial resistance. The problem of bacterial resistance to…